|
P200
LOADING...
#Digital Chip Card Locker: In The Service Of Building A Trusted System
#DCCL + End-to-end encryption
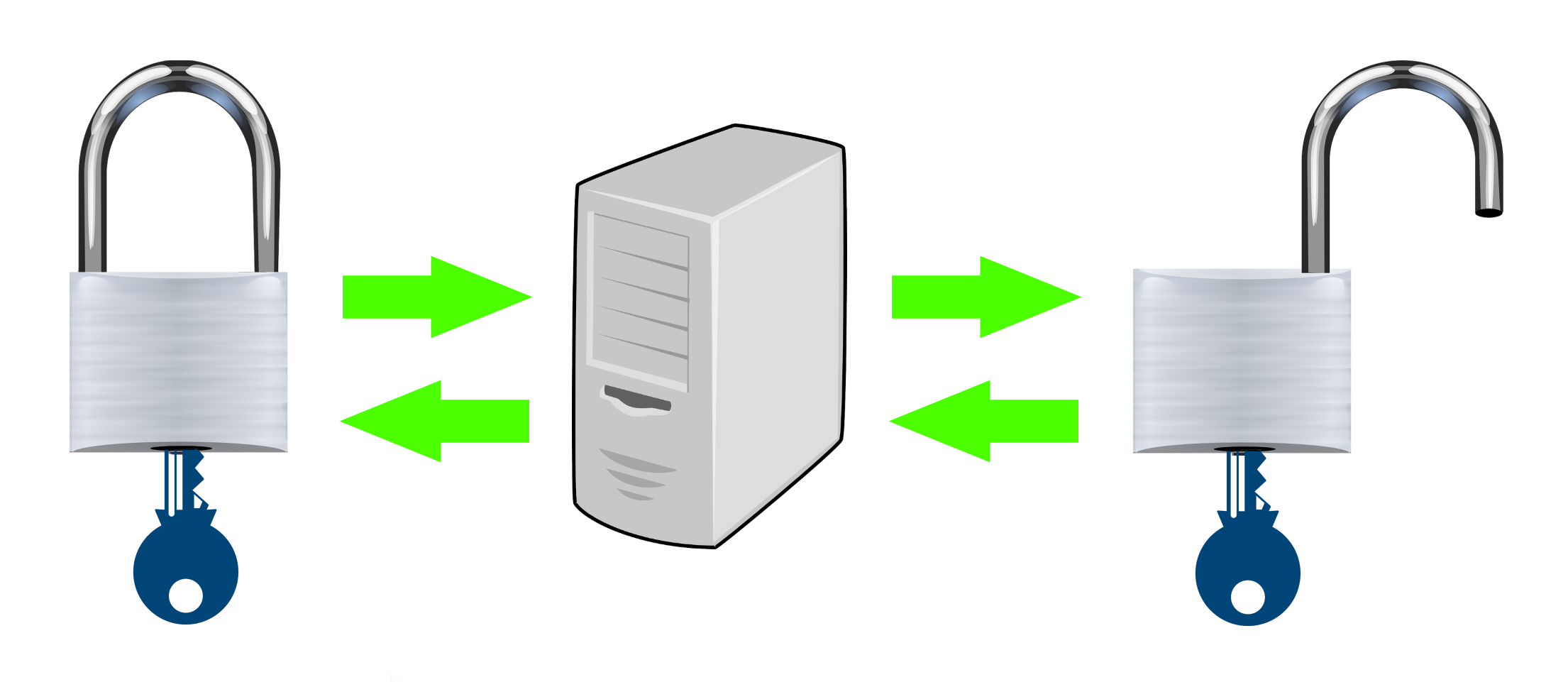
To ensure trusted encryption of transferred files and messages, ChatLiner relies on Digital Chip Card Locker technology, or DCCL for short.
DCCL is represented by a group of mathematically based algorithms that set the highest standards for online data protection.
The applied mathematical tools have implemented end-to-end encryption that includes the logarithmic function and the exponential function as mutually inverse functions.
#What is a DCCL key?
Digital Chip Card Locker utilizes algorithms to generate an encryption key consisting of up to 150 randomly generated digits divided into chunks and is secure and efficient for encrypting both short messages and files with large amounts of data.
The DCCL key and the corresponding mathematical logarithmic formula are responsible for encrypting and decrypting data distributed via the ChatLiner messaging platform.
#DCCL + RSA
#How does ChatLiner prevent data breach?
To decrypt files and messages encrypted by ChatLiner, one must be able to reproduce the DCCL encryption key and obtain the corresponding private RSA key.
Due to the rule that the DCCL encryption key and private RSA key can only be stored locally on your device, not on any other device, and not in the cloud, it is unlikely that anyone could ever come up with a solution to trick ChatLiner or make it vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
A ChatLiner-based system cannot be manipulated, no matter how hard someone tries to eavesdrop on the communicating parties, or intercept, decrypt, redirect, and modify files and messages exchanged via the platform.
#End-to-end encryption in the truest sense of the word: ChatLiner, at your service
 #ChatLiner is an open-source platform that provides authentic end-to-end encryption of transferred files and messages and prevents their modification, loss, damage or misuse.
There is no compromise, interception or collection of users' personal data or sensitive data from users' devices.
|